Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials Volume 64, December 2016
The study, “Mechanic and surface properties of central-venous port catheters after removal: A comparison of polyurethane and silicon rubber materials,” of the correlation between polyurethane (TPU) and silicone rubber (SiR) catheters and the susceptibility of degradation of the surface of reviewed catheters when influenced by the exposure to various chemo-therapeutic solutions.
A correlation between material properties and clinical performance was proposed. The surface morphology and chemical composition of the polyurethane catheter materials can potentially result in increased susceptibility of the catheter to bloodstream infections and thrombotic complications.
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials Volume 64, December 2016
Abstract
Central venous port devices made of two different polymeric materials, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) and silicone rubber (SiR), were compared due their material properties. Both naïve catheters as well as catheters after removal from patients were investigated. In lab experiments the influence of various chemo-therapeutic solutions on material properties was investigated, whereas the samples after removal were compared according to the implanted time in patient. The macroscopic, mechanical performance was assessed with dynamic, specially adapted tests for elasticity. The degradation status of the materials was determined with common tools of polymer characterisation, such as infrared spectroscopy, molecular weight measurements and various methods of thermal analysis. The surface morphology was analysed using scanning electron microscopy.
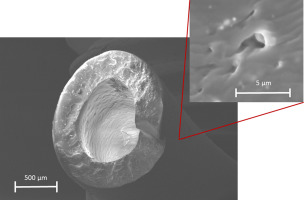
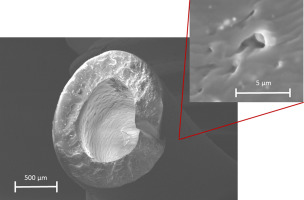
A correlation between material properties and clinical performance was proposed. The surface morphology and chemical composition of the polyurethane catheter materials can potentially result in increased susceptibility of the catheter to bloodstream infections and thrombotic complications. The higher mechanic failure, especially with increasing implantation time of the silicone catheters is related to the lower mechanical performance compared to the polyurethane material as well as loss of barium sulphate filler particles near the surface of the catheter. This results in preformed microscopic notches, which act as predetermined sites of fracture.
Graphical abstract
Introduction
The use of artificial elastic, polymeric materials in medical application is a wide field ranging from short time applications, such as cardiac or urinal catheters, up to long time implants (spines, ventricles) or complex components, such as defibrillator or pacemaker leads (Wintermantel and Ha, 2009). It is a major challenge to guarantee the functionality and stability as well as the biocompatibility of these materials (dependent on their use and application) at simultaneous patient comfort (ISO 10993). Due these complex requirements for materials and components, only interdisciplinary research can reveal failure mechanisms and offer solutions for improvement of materials.
For patients with chronic illness central venous catheters (CVCs) enable easy and safe venous access for laboratory testing, drug delivery and parenteral nutrition (Baskin et al., 2009). Depending on the duration of implant as well as various patient-specific factors, various catheter-related complications such as thrombosis, catheter associated infection or catheter leakage/rupture limit their use. Central venous port catheters, which remain implanted from months to years, pose special requirements to the used material in terms of stability, anti-thrombogenic and anti-infectious properties (Walser, 2012). Catheter related thrombosis and infection are the most frequent complications that require emergent removal of a central venous port catheter (Wildgruber et al., 2015). The ideal catheter is highly flexibly, yet stable and chemically inert over a long time period, and is not prone to thombosis or infection. Up to now, no rubber material fulfils all these requirements. Nowadays catheter materials frequently consist of polyurethane or silicon rubber materials. A comparison of 698 implanted venous-access ports of both materials implanted at the forearm (Wildgruber et al., 2016) observed that catheter-related bloodstream infections as well as thrombotic complications occurred significant more frequently with polyurethane catheters. In contrast to this the silicon trend to exhibit increased mechanic failure, such as disconnection or catheter rupture. Of note, this observation was limited to brachial port devices and catheters, which experience different mechanical forces compared to chest port placement. However the fact that significant differences were noted with respect to the used catheter material shows a potential impact of rubber material on catheter related complications.
In this study, we focus on the material-related differences of both polymeric materials to explain a possible structure-property relationship. Two different rubber materials commonly used as central venous port catheters in predominantly oncologic patient populations were investigated with respect to mechanic stability, physico-chemical degradation and surface properties of the rubber material. Catheter material was investigated in its’ native state and after incubation in a lab experiment in various chemotherapeutic solutions. Additionally, catheters explanted from patients after various duration of intravenous placement were investigated.
Research Snippets
Catheter Rubber Material
Two different types of port catheter materials were investigated. Silicon port catheters were purchased from Cook Medical, Bjaeverskov, Denmark (SiR catheters) and polyurethane catheters were obtained from PFM Medical, La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland (TPU catheters). Both catheters are established for use as central venous port catheters, implanted either pectorally or at the forearm. Catheters investigated were of similar diameter (SiR:5.0 French=5/3 mm, TPU:4.8 French=1,6 mm). Identification of…
General aspects of Port A Cath
Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPU) consist of linear aromatic or aliphatic polyurethane chains (hard segments) and of linear, aliphatic polyether, polyester or polycarbonate chains (soft segments). The choice and length of these chains are responsible for the material characteristics (Table 1, left column). Dependent on the structure of hard and soft segments crystalline and amorphous domains can be formed, which define the material stiffness and stability. Due to a large number in variation…
Conclusions
The article presents a material comparison of commonly used central venous port catheter material based on polyurethane and silicone for dedicated application of chemotherapy. The influence of various chemotherapeutic solutions was investigated, as well as catheters, which were implanted in patients for various times (three months to eight years). The material assessment was performed by cyclic mechanical tests and suitable methods for analysis of material degradation mechanism, such as thermal…
Research by
Ulrike Braun a, Edelgard Lorenz a, Christiane Weimann a, Heinz Sturm a, Ilham Karimov b, Johannes Ettl c, Reinhard Meier d, Walter A. Wohlgemuth e, Hermann Berger b, Moritz Wildgruber bf
aBAM Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, Unter den Eichen 87, 12200 Berlin, Germany
bDepartment of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Klinikum rechts der Isar, TU, München, Germany
cDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Klinikum rechts der Isar, TU, München, Germany
dDepartment of Radiology, Universitätsklinikum, Ulm, Germany
eDepartment of Radiology, Universitätsklinikum, Regensburg, Germany
fDepartment of Clinical Radiology, Universitätsklinikum, Münster, Germany